 |
SN 441011 standard Swiss plugs and sockets |
 |
SN 441011 standard Swiss plugs and sockets |
|
Plugs
and socket-outlets for household use, defined by SN 441011:2019
(formerly SEV 1011*) are used in Switzerland and Fürstentum
(Principality) Liechtenstein only.
* Schweizerischer Elektrotechnischer Verein (SEV), founded in 1889; renamed Electrosuisse in 2002. |
 |
Related
pages: heavy duty / 3-phase types |
 |
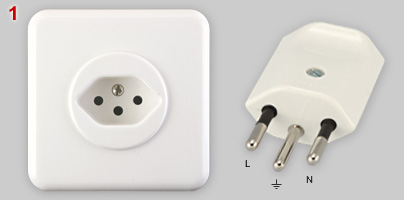
Swiss domestic plugs have a distinctive
hexagonal shape. The design dates back to the late 1930s. T11 and T12
were introduced in 1953, T23 in 1998 (T = Typ). Derived three-phase plugs - T15 (1979) and T25 (1998) - are shown in the Swiss heavy duty page. Shape of IEC 60906-1 plugs (proposed international plug standard, published in 1986) is based on Swiss T12, but pin diameter and earth pin offset differ. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|
| 1 | Standard
T13
domestic, recessed socket and matching T12 earthed plug. Rating: 10A -
250V. From 2017 it is no longer allowed to sell or install non-recessed sockets (see nos. 12 and 13). Plugs with partially insulated L and N pins have been introduced in 2009. Earth pins may not have insulating sleeves. From 2013 it is no longer allowed to sell T11 (see image 7) and T12 plugs without sleeves. T12 plugs are polarized plug because of the off-center position of the earth pin (line and neutral can't be reversed). Manufacturers: Feller AG (socket) and Max Hauri AG (plug). Corresponding logos are shown below. |
| note |
Also non-recessed T12 sockets exists (see
image 14), but from 2017 it is no longer allowed to sell these sockets. |
| 2 | T12 plug with side cord entry. Design and manufacturer: Max Hauri AG. |
| 3 | T13 connector plug for T12 plugs. See also no. 6. Manufacturer: Max Hauri AG |
| 4 | T23 socket
and plug rated at 16A - 250V. The rectangular pins prevents the
use of
T23 plugs in 10A T13 sockets or connectors, but the other way
round, 10A T12 round pin plugs fit in T23 sockets. 16A plugs do not have partially insulated L and N pins, because 16A sockets have always been recessed. Manufacturers: Amacher AG (socket) and WAROB, trademark of PWF Kunststofftechnik AG (plug). |
| 5 | 16A
T23
connector plug for either T12 or T23 plugs. Manufacturer: Max Hauri
AG., but the connector has a TH logo From ca. 2000 Max Hauri owns the
Tschudin & Heid trade-mark and produces the line of TH plugs. |
| 6 | Although
each of the three pins of T12 plugs have the same length, the earth pin
makes contact first when a plug is inserted in a T13 socket or
connector. The inside view of a T13 connector shows that the earth
contact position is 5 mm ahead of L and N contacts. The advanced
position applies also to T23 sockets and connectors. Manufacturer: Max
Hauri AG. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 7 | T13
socket with RCD. A Residual Current Device measures the difference
between current flowing through line conductor and the returning
current through the neutral conductor. If these do not sum to zero,
there is a leakage of current to somewhere else and disconnects the
circuit sufficiently quick to prevent a serious electric shock. The
device has a test button (yellow) and reset switch (dark grey).
Manufacturer: Feller AG (former AFH, now part of Schneider Electric). {PdV} |
| 8 | Extension cord with T11 plug and T11
connector, rated at 10A - 250V. From 2009 selling of rewireable plugs
and connectors without protective earth is no longer allowed. Only
T11extension and appliance cords with non-rewireable, moulded plugs are
still
available. Plugs must have insulating sleeves. The connector has shutters. T11 plugs fit in T13 and T23 sockets, as well as phased out T12 sockets (see image 13). Not earthed wall sockets have been taken off market in 1955. Manufacturer: Max Hauri AG. {PW} Dimensions of the T11 extension cord plug are similar to 2.5A Europlugs (Swiss SN EN 50075, also indicated as T26). The crucial difference between a T11 and T26 cord is the wire diameter: at least 1.0 mm2 for T11, whereas 0.75 mm2 is allowed for T26. |
| 9 | The image shows a T11 Schalenstecker
that consists of two shells and a holder with two pins. Pins do not
have screws to fix wires, instead wires have to be joined with solder.
Wiring and
assembling shells results in a T11 plug that can't be rewired. Since Schalenstecker
are non-rewireable, an image
processing program has been used to "assemble" the T11 plug shown in
image 9. The Schalenstecker is a patented design by Max Hauri and is used only for the Plug Rework Service offered by Max Hauri AG. Plug Rework Service means converting electrical equipment to Swiss standards. The original non-swiss plug is replaced by a T11 or T12 plug. The museum is grateful to Max Hauri for donating a T11 Schalenstecker, a model that is nowhere for sale. {PW} |
 |
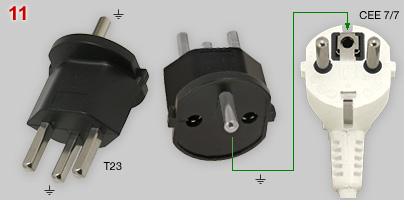 |
| 10 - 12 |
Electrical
equipment, made by
continental European manufacturers often have appliance cords
with a moulded earthed (CEE 7/7) or non-earthed (CEE 7/17) hybrid
Schuko plug. Fix-Adapters offer a simple method for using non-Swiss appliance cords in Switzerland. Image No. 10 shows a T11-CEE 7/17 (10A). The Fix-Adapter has two plastic pins. They prevent using the not earthed adapter for earthed CEE 7/7 plugs. Image No. 11 shows a T23-CEE 7/17 (16A) model Image No. 12 CEE 7/7 and 7/17 Fix-Adapters are also available with a 10A T12 plug. A plug inserted in a Fix-Adapter can't be removed because of a ring of metal barbs in each pin contact holes (see image 10, inset). CEE plug and adapter form a permanent couple. An alternative would be the use of a travel adapter, but in Switzerland they are allowed only for temporary use. Using Fix-Adapters is restricted to indoor purposes. Manufacturers: Werkstatt für Gestaltung, WfG AG (nos 10, 11) and Steffen AG (No. 12) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 13, 14 |
Image 13 illustrates that using a plug without insulating
sleeves in combination with a non-recessed T12 socket is potentially
dangerous. Image 13 show two
classic, flush type T12 sockets. Left: single outlet socket. Right: an
elegant triple outlet T12 socket
(also available as recessed T13 socket model). Manufacturers: image 12: Feller AG (socket) and unknown company (plug) using logo q (see below); image 13: Electro-Mica AG (socket left) and Amacher AG (triple outlet socket). The use of recessed T13 sockets* minimizes the risk of electrocution, but non-recessed T12 sockets can still be found in many older homes. That was an important reason to introduce plugs with partially insulated line and neutral pins in 2009. Selling plugs with non-isolated pins was prohibited four years later. * recessed triple outlets are nowadays available for T13, and a similar model for T23 also. |
| 15 | 3-way T12 multi plug. Production of the model ended mid 1990s, because it had a serious safely problem. It is possible to insert only one pin of a T11 or Europlug. Depending on the appliance attached to a flex cord, touching the other - free - pin may result in an electric shock. The manufacturer of the multi-plug is not indicated. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 16 | Out of
date
Swiss T1 plug, rated at 10A-250V. From 1 January 2000 it is no longer
allowed to sell or install type 1 plugs. Instead T12
plugs have to be used (or moulded T11, see image 8). Manufacturer: unknown company that used a logo with P and M (see logo p below). |
| 17 | Difference
between a T12 and T1 plug. The rectangular
shape of T1 plug No. 16 makes it impossible to use it in recessed
sockets. T1 plugs can only be used in T12 sockets, which are gradually
phased out. Manufacturer of the white T12 plug: Tschudin & Heid. |
| 18 | Example
of a round, unusual flat T1 plug with cord side entry. Rating: 10A -
250V. Wires have to be twisted trough grooves in the pin top (see
inset). Inside the plug there is insufficient space for screws to
faster wires more securely. The ASEV mark could indicate that plug has been made in Switzerland. The unknown company used a logo with a single H. |
| 19 | T12 plug, interesting from a historic point of view. The Italian company Bticino in Varese (close to the Swiss border) has attempted to penetrate the Swiss market. The shown plug, which has an old ASEV certification mark and classic Bassani Ticino logo, dates back to the 1990s. Although the plug quality is outstanding and complies fully with Swiss standards, Bticino has not been successful in realizing a viable market share; the company abandoned the Swiss marked rather soon. {ARF} |
 |
  |
  |
 |
| 20 |
Earthed T2 plug, introduced in the early 1930. Rating: 10A - 250V. Shown plug is an early 1950s model. T2 sockets had an earth pin, a system comparable to CEE 7/5*. Old Swiss, not earthed (T1) plugs with a round base (see nos. 18 and 31) cannot be inserted in a T2 socket because of the earth pin. The other way round, an earthed T2 plug fits into a not earthed T1 socket (see no. 28), but the security provided by the earth connection is broken. To avoid this potentially dangerous situation a new type of earthed plug has been designed in 1937 and introduced in 1953 (see no. 21). Manufacturer: unknown company, using a logo with M and W (see logo 'o' below). {EA} * Offset of earth contact: Swiss T2 / T14 = 13.6 mm; CEE 7/5 = 10.2 mm; Swiss T12 = 5 mm. |
| 21 | T12
earthed plug, introduced in 1953. Besides the earth pin that switched
position from socket to plug, the hexagonal plug shape was introduced also. Manufacturer: J.J. Buser AG (Basel). |
| 22a, b |
When
earthed T2 plugs and sockets were replaced by T12 plugs and T13 sockets
in 1953, a "transition" T14 socket was introduced that accepts both
old T2 and new T12 plugs. T14 sockets were available until
1975. Manufacturer:
Feller AG {EA} The inner part of the T14 socket is shown in image 22b. |
| 23 | Flush
socket providing switch, not earthed razor socket and T14 socket.
The additional razor socket is convenient because it accepts both old
type (non-hexagonal) T1 plugs and modern T11 plugs. Switch and outlets can be wired sparately. Manufacturer: Adolf
Feller AG in Horgen (AFH). {PdV} |
| 24 |
T12
adapter plug with two T14 outlets that accept old T2 and modern T12
plugs. Manufacturer: F. Baillod S.A. {FS} |
note |
A comparable T20 "transition" socket for 10A-380V T4 plugs (with earth contact) and T18 plugs (with earth pin) is shown on the Swiss heavy duty page (see image no.8). |
 |
 |
 |
| 25 - 27 | Different electricity tariffs for domestic
lighting, heating and equipment driven by an electric motor were quite
common in Switzerland. For special tariffs, three T12 plug variants
have been designed: T12a with two flat power pins in tandem position (flach-flach waagrecht Nebentyp) for heating; see image no. 25. {RD} T12b with two flat power pins in parallel position (flach-flach senkrecht Nebentyp) for lighting; see no. 26. T12c with a flat and round power pin (flach-rund Nebentyp) for motor driven equipment; see no. 27. Standard T12, with three round pins, can be used for each purpose (source). Rating of T12, T12a, T12b and T12c: 10A - 250V. Size of flat pins = 4.0 x 2.5 mm; round pins have a diameter of 4.0 mm.. T12a is a "transition" model that could be used with old sockets that had an earth pin, but the plug has also a earth pin, introduced in 1953. The use of Nebentypen lasted until 2012, but for some time the three types remained available for replacement. Manufacturer of plug no. 25: unknown company that uses logo with P and M (see logo 'p' below). Plugs nos 26 and 27 have been ordered in 2016 by F. Baillod S.A. |

|

|

|

|
| 28 | Classic,
Bakelite T1 socket, rated at 6A - 250V. Socket has a 14 mm deep recess. Manufacturer: Adolf Feller in Horgen (AFH). Dating: 1930s. {PdV} |
| 29 | Classic, Bakelite T1 plug, rated at 6A - 250V. The plug, that has an older type ASEV certification mark, has been made for the Swiss company SOLIS, designer and manufacturer of domestic appliances. It is unknown which company has made the plug. Dating: 1950s - '60s. {WN} |
| 30 | Bakelite 6A - 250V plug. Production of round base plugs in Switzerland ended when hexagonal plugs and sockets were introduced. The plug has an ASEV certification mark and an unknown manufacturer's logo with a B and K, or R (see logo n below). Dating: probably early 1950s. {WN} |
| 31 | Classic,
Bakelite earthed plug with Swiss T12 pin configuration. The plug has an
unusual low
rating of 2A - 250V. Manufacturer: German company Frankl & Kirchner. The German MPAD mark, indicating origin and type of Bakelite casts suggests that the plug dates back to the 1950s. It does not have any certification mark. {WN} |
Marks and logos shown on Swiss plugs and sockets in the museum collection are depicted in images a - q. Companies that use thier full name have been left out (i.e. Amacher, WAROB and Solis). More information about Swiss manufacturers is given in a separate list. |
 |
 |
| a b c |
The Association Suisse des Électriciens (ASE) / Schweizerischer Elektrotechnischer Verein (SEV), founded in 1889, is active on promotion and testing of function and safety of electrical installations and appliances. Certification mark 'a' has been introduced In 1929. The association renamed Electrosuisse in 2002 and the old certification mark was replaced by type 'b'. Occasionally SEV conformity symbol 'c' can be found. |
| d | F. Baillod S.A. in La Chaux-de-Fonds (NE) | Logos of unknown, probably Swiss,
manufacturers: |
|
| e | Brac AG in Breitenbach (SO) |
||
| f | Electro-Mica AG in Mollis (GL) | o | found on an old T12 plug (not shown) |
| g | Feller AG in Horgen (ZH), classic AFH logo | p | found on T2 plug shown in image 20 |
| h | Feller AG in Horgen (ZH), modern logo | q | found on T12 plug shown in image 13 |
| i | Frankl & Kirchner (now Efka) in Schwetzingen, Germany | |
|
| j | Max Hauri AG, Bischofszell (TG) | |
If you recognize a logo, please inform me. |
| k | Plastri-Mayer GmbH in Tochtelfingen, Germany |
Find my address at the start page. | |
| l | A. Steffen AG in Spreitenbach (ZH) | ||
| m | Tschudin & Heid in Waldenburg (BL) | ||
| n | Werkstatt für Gestaltung, WfG AG in Zürich
(ZH) |
|
|
|
|
|
|