 |
Certification Marks on plugs and sockets |
info page |
 |
Plugs usually have one ore more
certification marks. They show that the plug meets the safety standards
as specified in the given country. Older CEE 7/x and IEC plugs had many marks, necessary to sell products throughout Europe. Nowadays certification in one of the countries of the European Union applies to each of the EU states. Images below shows certification marks that have been found on plugs and sockets in the museum collection. Moreover four Asian marks have been added, based on plug photos sent by Jonathan Miles Besides certification marks there is often a logo of the manufacturer. Lists of manufacturers give logos and company details. Other marks that occasionally can be found on plugs and sockets are: CE, ENEC and RoHS. Explanation is given at the bottom of page. Example left, with 12 marks, is an IEC 60320 appliance connector made by Well Shin Technology Co., Ltd in Taipei Taiwan. |
| European certification marks |
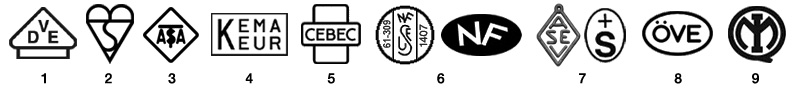 |
 |
 |
| 1 | Germany: VDE = Verband Deutscher Elektrotechniker. |
| 2 | United Kingdom: Kitemark, owned and operated by the British Standards Institution (BSI). |
| 3 | United
Kingdom: ASTA Diamond mark issued by Association of Short-Circuit
Testing Authorities (trom 2007 part of Intertek Group). |
| 4 | Netherlands: KEMA = Keuring van Elektrotechnische Materialen te Arnhem (from 2011 part of the Norwegian DNV GL Group). |
| 5 | Belgium: CEBEC = Comité Electrotechnique Belge / Belgisch Electrotechnisch Comité; division of SGS Belgium (Société Générale de Surveillance). |
| 6 | France: USE =
l'Union des Syndicats de l'Électricité (certification
numbers differ per device). Mark used from 1924 until 1996. France: product meets standards of NF = Norme Française. Mark issued by AFNOR (l'Association Française de Normalisation). |
| 7 | Switzerland:
ASE/SEV = Association Suisse des Électriciens / Schweizerischen
Elektrotechnischer Verein (mark used until 2002). Switzerland: after renaming the association 'Electrosuisse' in 2002 the +S certification mark is introduced. |
| 8 | Austria: ÖVE = Österreichischer Verband für Elektrotechnik. |
| 9 | Italy: IMQ = Istituto Italiano del Marchio di Qualitŕ |
| 10 | Denmark: DEMKO mark (Danmarks Elektriske Materielkontrol). |
| 11 | Norway: NEMKO mark (Norges Elektriske Materiellkontroll). |
| 12 | Sweden: SEMKO mark (Svenska Elektriska Materielkontrollanstaiten). |
| 13 | Finland: FIMKO mark (issued by Suomen Standardisoimisliitto). |
| 14 | Luxemburg: SNCH mark = Société Nationale de Certification et d'Homologation |
| 15 | Spain: AENOR = Asociación Espagńola de Normalización y Certificación. |
| 16 | Portugal: CERTIF mark = Associaçăo para a Certicaçăo. |
| 17 | Czech Republic: EZU mark = Elektrotechnický zkušební ústav (Electrotechnical Testing Institute). |
| 18 | Slovakia: EVPU mark = Elektrotechnický výskumný ústav a projektový (Electrotechnical Research Company). |
| 19 | Poland: B mark = Polskie Centrum Badan I Certyfikacji (Polish Centre for Testing and Certification). |
| 20 | Hungary: MEEI mark = Magyar Elektrotechnikai Ellenörzö Intézet (Hungarian Institute for Testing Electrical Equipment). |
| 21 | Ireland: NSAI mark = National Standards Institute. |
| 22 | Germany: TÜV Rheinland mark = Technischer
Überwachungsverein (Technical Inspection Association, also involved in
certification). |
| 23 | Russia: GOST-R mark = Gosudarstvennyi Standarty Rossiiskoi Federatsii (Federal Agency on Technical Regulating and Metrology). |
| 24 | Russia,
Belarus, Armenia, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan: EAC = Eurasian Conformaty
mark (EAC has replaced GOST-R in 2010). |
| 25 | Slovenia, SIQ = Slovenski Institut za kakovost in meroslovje (Slovenian Institute of Quality and Metrology} |
| Selection of non-European certification marks |
 |
 |
 |
| 50 | United States of America: UL mark = Underwriters Laboratories Inc. |
| 51 | Canada: CSA mark = Canadian Standards Association. |
| 52 | Mexico: NOM mark = Normas Officiales Mexicanas - Asociación de Normalización y Certificación. |
| 53 | Brazil: INMETRO mark = Instituto Nacional de Metrologia, Qualidade
e Tecnologia (National Institute of Metrology, Stadardization and Industrial Quality). CEPEL = Centro de Pesquisas de Energia Elétrica (Research Centre for Electrical Energy). |
| 54 | Uruguay: UNIT mark = Instituto Uruguayo de Normas Técnicas. |
| 55 | Argentina: IRAM and S-mark (Instituto Argentino de Normalización y Certificación); both IRAM and S- marks can be found on plugs. |
| 56 | Chile: SEC mark = Superintendencia de Electricidad y Combustibles (Superintendence of Eletricity and Fuels). |
| 57 | South Africa: SABS mark = South African Bureau of Standards. |
| 58 | Turkey: TSE mark = Türk Standardlari Enstitüsü (Turkish Standards Institution). |
| 59 | Israel: SII mark = Standards Institution of Israel. |
| 60 |
Saudi Arabia and
Gulf states Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, United Arab Emirates and Oman: GCC
mark, issued by Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Standardization Organization (GSO). |
| 61 | India: ISI mark = Indian Standards Institute. |
| 62 | India: STQC mark =
Standardization Testing and Quality Certification, issued by the
Government of India Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology. Mark may have the word 'Certification' in Hindi. |
| 63 | Malaysia: MS mark = SIRIM Berhad (Standards and Industrial Research Institute of Malaysia). |
| 64 | Thailand: TISI mark = Thai Industrial Standards Institute. |
| 65 | Singapore:
Safety Mark issued by Enterprise Singapore, the national standards and
accreditation body. The mark consists of a square (shown) and rectangle with words SAFETY MARK and certification number. |
| 66 | Peoples Republic of China: CCC mark = China Compulsory Certification. |
| 67 | Hong
Kong: HK mark = Hong Kong Safety Mark, issued by the Hong Kong
Standards and Testing Centre (STC) |
| 68 | Japan: PSE mark = Product Safety Electric Appliance and Materials. |
| 69 | Australia and New Zealand: RCM mark = Regulatory Compliance (trademark owned by Australian and New Zealand regulators). |
| 70 | Morocco: CMIM mark, ensuring that
industrial products, among others low voltage electrical equipment,
comply with safety standards. |
 |
CE
mark Conformité
Européenne / European Conformity. EU regulations allow company-internal self-certification processes. The results of tests that show that the product meets the relevant requirements on safety, health and environmental issues must be documented. Moreover, the company has to take responsibility for the safety of the product. This self-certification system applies to many electrical and electronic products, but domestic plugs and sockets are specifically excluded from the scheme. Sources: European Commission, Wikipedia. Domestic plugs and sockets are subject to national standards and regulations. Nevertheless you will find CE marks occasionally on plugs. |
|
 |
UKCA mark
United Kingdom Conformity Assessed marking. The UKCA certification
marking was introduced when the UK left the European Union. The UKCA
scheme will initially follow those for CE marking, but from 2021 the
two schemes may diverse. An adapted - UKNI - version if effective in
Northern Ireland. Wikipedia UKCA
/ UKNI entry gives additional information. |
|
 |
Unofficial mark Occasionally found on plugs and sockets made in China. This fake mark has no legal status. The look may suggest that it is an European Conformity mark, but the spacing between C and E is different. It is neither a "Chinese Export" mark. The official Chinese Certification mark (CCC) is show in the list above; see no. 66. |
|
 |
ENEC mark European Norms Electrical Certification. Products that have received ENEC approval comply with applicable European safety standards. You may find this mark among others on household appliances, consumer electronics, batteries and portable tools, but it is uncommon on plugs and sockets. | |
 |
RoHS mark Restriction of Hazardous Substances. European Union directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment. The directive is a guide; implementation may differ between EU countries. See Wikipedia RoHS page for details. |
|
|
|
|
|
|